The Role of AI in Robotics: From Industrial to Domestic Applications During the 1980S
The role of AI in robotics during the 1980s marked a significant leap from industrial applications to domestic settings. In factories, AI-enabled robots began executing complex tasks with high precision due to advances in sensors and machine vision systems. Concurrently, the advent of domestic robots like RB5X and Topo revolutionized household chores. What specific innovations facilitated these transitions, and how did they lay the groundwork for today's smart home technologies? Let's delve into these pivotal developments further.
Industrial AI in Robotics
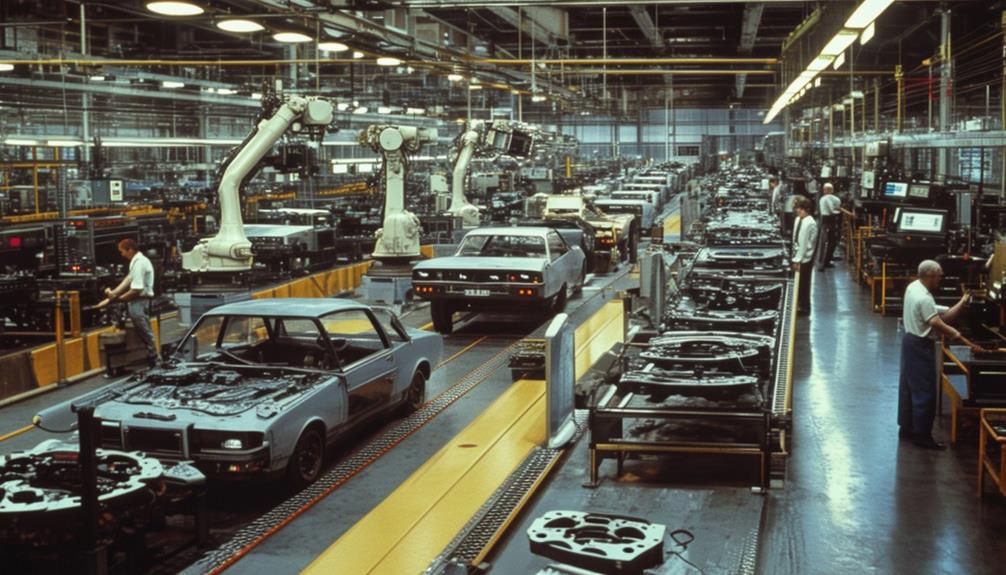

In the 1980s, industrial AI in robotics advanced significantly with improvements in sensors and machine vision systems, enabling robots to perform tasks like painting and arc welding with greater precision and efficiency. AI began to transform industrial robots from mere tools to intelligent systems capable of sophisticated operations.
The era saw the rise of industrial robots equipped with enhanced sensors, which improved their ability to perceive and interact with their environments. This technological leap allowed robots to execute tasks with a previously unattainable level of precision. Machine vision systems were another critical advancement, providing robots with basic visual processing capabilities. These systems utilized early forms of machine learning to interpret visual data, enabling robots to identify and manipulate objects in their workspace.
The integration of advanced microprocessors during the 1980s further increased the efficiency and versatility of industrial robots. These improvements allowed robots to perform complex tasks quickly and accurately, reducing the need for direct human intervention in hazardous or repetitive tasks. By the late 1980s, industrial robots had become indispensable assets in various industries, revolutionizing manufacturing processes and enhancing task efficiency.
Sensor Integration
Building on the innovations of the 1980s, sensor integration became crucial in transforming industrial robots into intelligent, adaptive systems. The integration of sensors such as proximity sensors and tactile sensors significantly enhanced robots' decision-making capabilities. They could now gather real-time data, interact more effectively with their environment, and adjust their actions dynamically.
This technological advancement enabled industrial robots to undertake more complex tasks with unprecedented precision and efficiency. Robots began performing intricate assembly jobs and quality checks that were previously unmanageable. The ability to sense and react in real-time allowed these robots to handle diverse tasks autonomously, thereby boosting productivity.
Moreover, sensor integration improved human-robot interactions in manufacturing settings. Enhanced sensory capabilities made robots more aware of their surroundings, reducing the risk of accidents and making them safer to work alongside humans. This shift marked the advent of more intelligent and adaptive robots seamlessly integrated into the workforce.
Machine Vision Systems

Exploring machine vision systems in robotics reveals the foundational impact of early technologies from the 1980s on contemporary advancements. These systems have enabled robots to recognize objects and navigate environments, becoming essential in industrial applications. Understanding trends in industrial adoption highlights how machine vision has transformed automation and quality control, driving efficiency and precision.
Early Vision Technologies
In the 1980s, machine vision systems revolutionized industrial robotics by enabling real-time visual perception. By integrating cameras and sensors, these systems allowed robots to perform tasks like inspection and quality control with greater accuracy and efficiency. Real-time analysis capabilities enabled robots to quickly process visual information and respond accordingly.
Early machine vision technologies focused on object recognition using advanced image processing algorithms. These algorithms analyzed visual data captured by cameras and sensors to accurately identify and categorize objects. Improvements in hardware components, such as faster processors and more sophisticated sensors, significantly enhanced the speed and accuracy of these systems.
In industrial automation, machine vision systems transformed robotic operations. Robots could now handle complex and varied tasks, increasing their versatility and functionality. Instead of being limited to repetitive, pre-programmed actions, industrial robots could adapt to changing environments and requirements. This adaptability was crucial for tasks requiring high precision and consistency, thereby improving productivity and reducing error rates. By the end of the 1980s, machine vision systems had become essential tools in industrial automation.
Industrial Adoption Trends
As the 1980s advanced, industries rapidly integrated machine vision systems, significantly transforming robotic capabilities and enhancing efficiency across various manufacturing processes. This era witnessed the rise of machine vision, which revolutionized automation by enabling robots to process visual input and make informed decisions. This technological breakthrough was fueled by advancements in imaging and computing power, allowing robots to inspect, identify, and guide components with unprecedented precision.
The swift adoption of machine vision systems led to remarkable improvements in quality control. Robots equipped with these systems could detect defects and inconsistencies with greater accuracy than human inspectors, ensuring higher product quality. Additionally, productivity saw a substantial boost, as robots with vision systems could operate faster and more reliably, reducing downtime and minimizing human error.
Autonomous Industrial Robots
Autonomous industrial robots transformed the manufacturing landscape of the 1980s by efficiently handling dangerous and precision tasks. Equipped with rudimentary sensors and machine vision systems, these robots significantly enhanced productivity and safety in industrial settings. The integration of microprocessors not only reduced costs but also enabled these robots to perform complex tasks with greater accuracy. Consequently, adaptable robotic systems emerged, capable of working alongside humans.
Here's a quick comparison of key features in 1980s autonomous industrial robots:
| Feature | Benefit | Example Task |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Vision Systems | Improved precision | Arc welding |
| Microprocessors | Cost reduction | Complex assembly |
| Precision Work | Enhanced product quality | Painting |
| Safety Improvements | Reduced human risk | Hazardous material handling |
| Adaptable Robotic Systems | Flexibility in operations | Product inspection |
These innovations laid the groundwork for the development of smarter robots in subsequent decades. By integrating machine vision systems, manufacturers achieved remarkable precision and productivity gains. The use of microprocessors allowed robots to handle increasingly complex tasks, making them adaptable to various industrial settings. The 1980s marked a pivotal era in robotics, with these autonomous industrial robots significantly advancing manufacturing technologies and setting the stage for future progress.
AI-Powered Domestic Robots
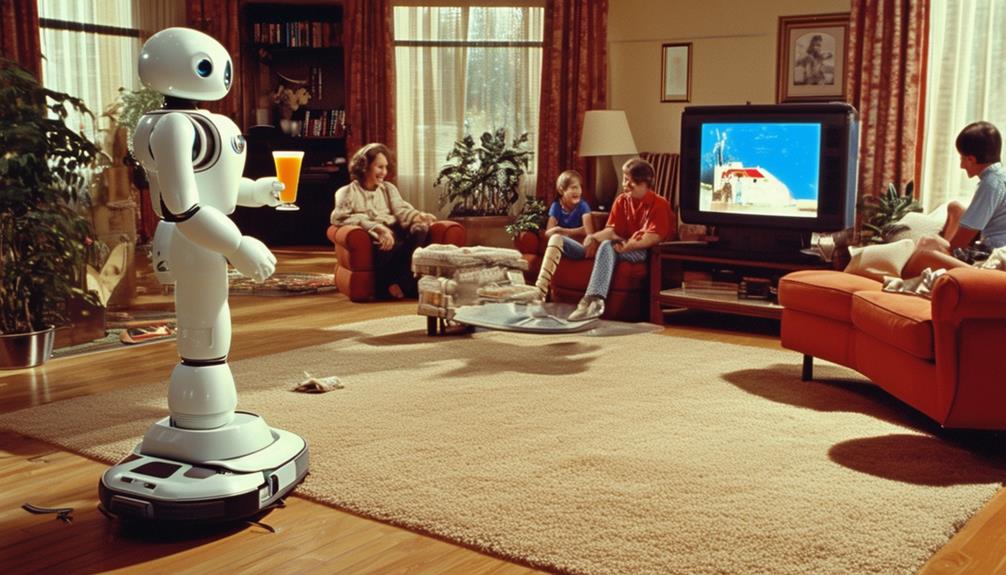

In the 1980s, AI-powered domestic robots like the RB5X and Topo began to simplify household chores by automating tasks such as cleaning and monitoring. These early robots used AI for navigation and interaction, adapting to changing environments. Their innovations laid the groundwork for today's smart home technology.
Early Domestic Innovations
Early domestic innovations in AI-powered robots, such as the Heathkit HERO series and the RB5X robotic arm, marked significant milestones in the evolution of smart home technology. These pioneering domestic robots demonstrated foundational AI capabilities that laid the groundwork for today's advanced home automation systems.
The Heathkit HERO series, particularly the HERO 1, was among the first commercially available humanoid robots. It featured programmable movements and could interact with its environment through voice recognition and object detection. This series illustrated the potential of AI in facilitating robotic assistance in everyday tasks. Meanwhile, the RB5X robotic arm, developed by Cincinnati Milacron, showcased the integration of industrial-grade robotics into domestic settings, emphasizing advanced capabilities in executing simple tasks.
These early domestic robots were not merely technological curiosities; they were practical tools that foreshadowed the future of smart home technology. They provided a glimpse into how AI could simplify and enhance daily living by assisting with routine tasks. Key features included:
- Voice recognition: Understanding and responding to verbal commands.
- Object detection: Identifying and interacting with various objects.
- Programmable movements: Customizing actions to meet diverse needs.
- Simple task execution: Performing basic household tasks efficiently.
These innovations underscored the potential of AI in transforming domestic environments, making life more convenient and efficient.
Household Chores Automation
In the 1980s, the advent of AI-powered domestic robots aimed to revolutionize household chores such as cleaning and cooking. These robots were designed to automate repetitive tasks, significantly easing daily life. Envision a domestic robot that not only vacuums your floors but also assists with meal preparation. Thanks to advanced AI algorithms, these robots could navigate obstacles, recognize objects, and optimize their performance, adapting to various household environments.
Here's a snapshot of how different tasks were automated:
| Task | Example Robots | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | RoboMaid, CleanBot | Navigate obstacles, recognize objects |
| Vacuuming | RoboVac, DustBuster | Intelligently map rooms, optimize cleaning paths |
| Cooking | ChefBot, CookAssist | Recipe management, precise ingredient handling |
These AI algorithms were transformative, enabling domestic robots to learn and adapt to home environments. They could efficiently map out rooms for vacuuming and manage recipes for cooking, ensuring tasks were performed optimally. By automating chores like cleaning, vacuuming, and cooking, these early domestic robots marked a significant leap toward convenience and efficiency in household management.
Domestic Applications
As AI technology advanced in the 1980s, domestic robots like Electrolux's Trilobite began revolutionizing household chores with autonomous vacuuming and lawn mowing. This era marked a significant shift from industrial-focused robotics to consumer-oriented AI applications. These early domestic robots relied on AI algorithms and sensor technologies to navigate indoor spaces, avoid obstacles, and efficiently complete tasks.
The introduction of the Trilobite robotic vacuum cleaner was groundbreaking. It showcased how AI could be integrated into household chores, making life easier and more convenient. These autonomous robots were early examples of smart home technologies, setting the stage for today's sophisticated devices.
Key features of 1980s domestic robots included:
- AI algorithms: Enabled autonomous cleaning and navigation around furniture.
- Sensor technologies: Allowed for obstacle detection and avoidance.
- Autonomous operation: Eliminated the need for manual operation of vacuum cleaners and lawn mowers.
- Smart home integration: Paved the way for modern connected home environments.
Legacy of 1980s Robotics
The 1980s laid the groundwork for modern robotics by integrating advanced sensors and basic machine vision systems, revolutionizing both industrial and domestic applications. During this pivotal decade, industrial robots took on tasks like painting, arc welding, and handling hazardous operations, significantly transforming industrial manufacturing processes. The cost reduction of computer hardware, particularly microprocessors, played a crucial role in enabling these advancements.
As intelligent systems became more refined, robotics opened new opportunities in materials handling and intricate assembly operations. This period marked a shift toward the development of smarter industrial robots capable of performing complex tasks with greater precision. Additionally, these innovations fostered safer human-robot interactions, setting a precedent for future advancements in human-robot collaboration.
The legacy of 1980s robotics extends beyond industrial settings. Advances in AI and machine vision systems during this decade laid the foundation for more sophisticated AI applications in various fields. Today, the influence of 1980s robotics is evident in everything from automated manufacturing lines to everyday domestic robots. The intelligent systems initiated during this period have evolved, shaping the future of robotics and enhancing human-robot interaction across multiple domains.
Conclusion
The 1980s marked a pivotal era for AI in robotics, transforming both industrial and domestic applications. Advancements in sensors, machine vision, and microprocessors made robots smarter and more efficient. This period revolutionized factories and introduced intelligent robots like RB5X and Topo into homes, automating tasks and paving the way for future smart technologies. The innovations of the 1980s laid the foundation for the robotics advancements we enjoy today.




